一、ChnSentiCorp情感分析酒店评论数据集
ChnSentiCorp情感分析酒店评论数据集是一个标注了情感的数据集,分了负面和正面两类,下载地址:
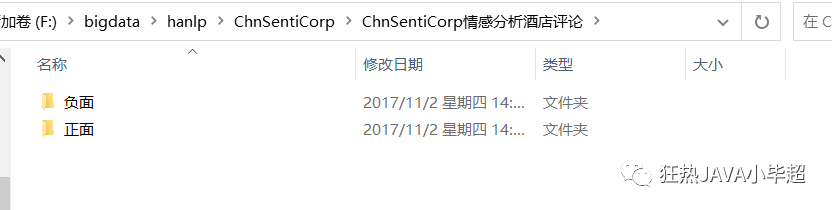
下载解压后结构:
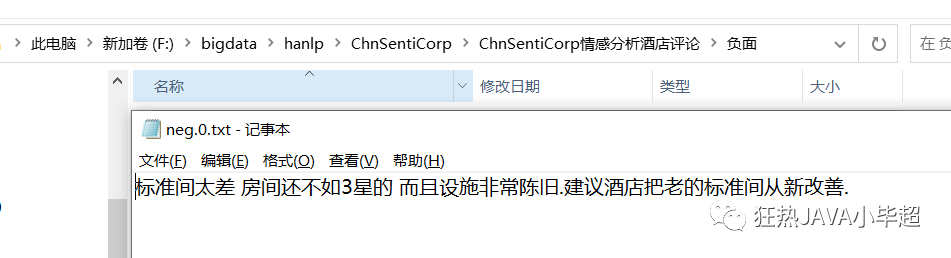
实例数据样例:
下面使用 HanLP 基于 SVM 支持向量机进行分类训练,有关于 HanLP 环境的搭建,可以参考下面这篇文章:
训练数据
public class ClassifySentimentTrain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//语料库的地址
String dataPath = "F:/bigdata/hanlp/ChnSentiCorp/ChnSentiCorp情感分析酒店评论";
//模型保存路径
String modelPath = "F:/bigdata/hanlp/ChnSentiCorp/svm-classification-model.ser";
//训练数据
trainData(dataPath, modelPath);
}
private static void trainData(String dataPath, String modelPath) throws IOException {
File corpusFolder = new File(dataPath);
if (!corpusFolder.exists() || !corpusFolder.isDirectory()) {
System.err.println("没有文本分类语料");
return;
}
// FileDataSet省内存,可加载大规模数据集,支持不同的ITokenizer,详见源码中的文档
// 使用前90% 的数据作为训练集
IDataSet trainingCorpus = new FileDataSet()
.setTokenizer(new HanLPTokenizer())
.load(dataPath, "UTF-8", 0.9);
// 创建SVM分类器
IClassifier classifier = new LinearSVMClassifier();
// 训练数据
classifier.train(trainingCorpus);
// 获取训练模型
AbstractModel model = classifier.getModel();
// 使用后10% 的数据作为测试集
IDataSet testingCorpus = new MemoryDataSet(model)
.load(dataPath, "UTF-8", -0.1);
// 计算准确率
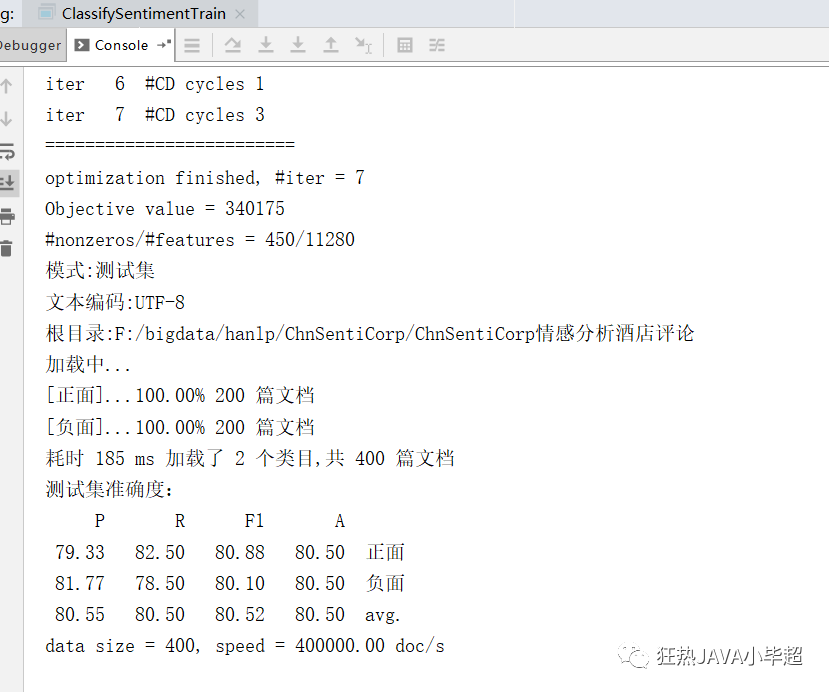
FMeasure result = Evaluator.evaluate(classifier, testingCorpus);
System.out.println("测试集准确度:");
System.out.println(result);
// 保存模型
IOUtil.saveObjectTo(model, modelPath);
}
}查看训练日志:
查看训练模型:
测试模型
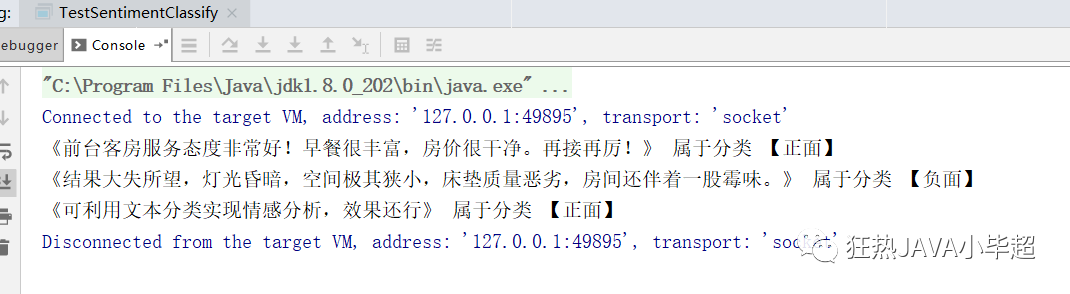
public class TestSentimentClassify {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String modelPath = "F:/bigdata/hanlp/ChnSentiCorp/svm-classification-model.ser";
testModel(modelPath);
}
private static void testModel(String modelPath){
LinearSVMModel model = (LinearSVMModel) IOUtil.readObjectFrom(modelPath);
IClassifier classifier = new LinearSVMClassifier(model);
// 测试分类
String text1 = "前台客房服务态度非常好!早餐很丰富,房价很干净。再接再厉!";
System.out.printf("《%s》 属于分类 【%s】\n", text1, classifier.classify(text1));
String text2 = "结果大失所望,灯光昏暗,空间极其狭小,床垫质量恶劣,房间还伴着一股霉味。";
System.out.printf("《%s》 属于分类 【%s】\n", text2, classifier.classify(text2));
String text3 = "可利用文本分类实现情感分析,效果还行";
System.out.printf("《%s》 属于分类 【%s】\n", text3, classifier.classify(text3));
}
}