内容
隐藏
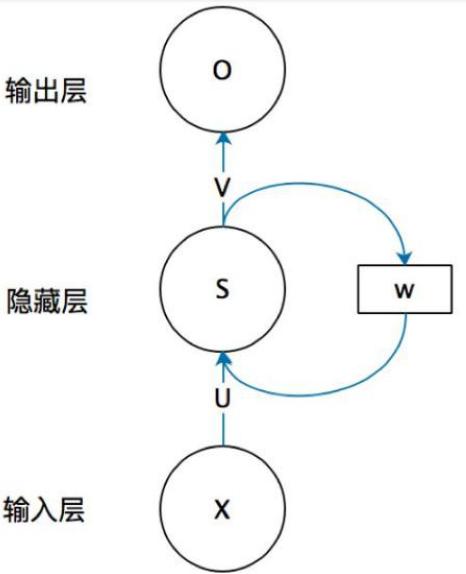
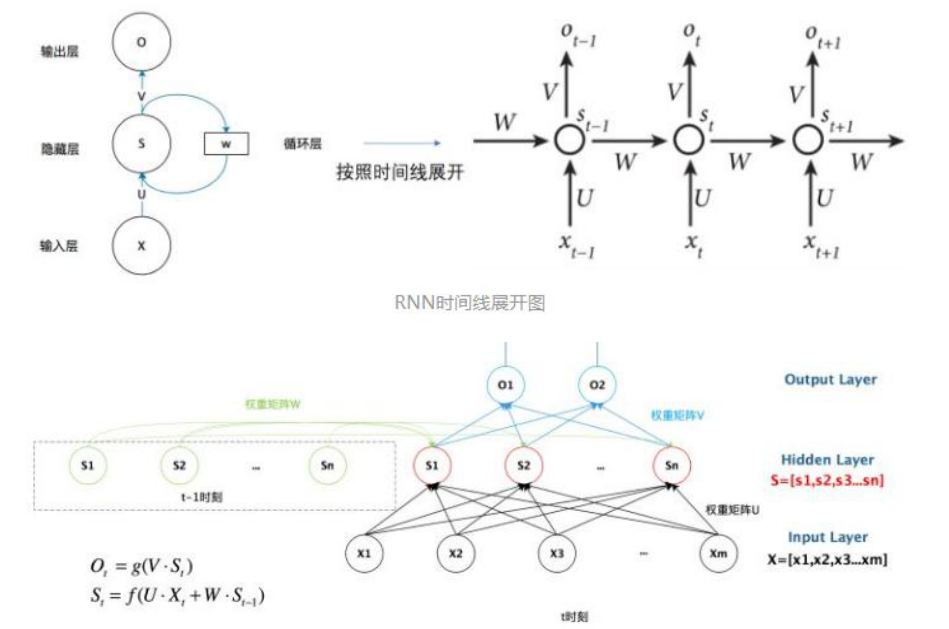
概念
为什么需要 RNN(循环神经网络)
DNN都只能单独的取处理一个个的输入 前一个输入和后一个输入是完全没有关系的。
但是,某些任务需要能够更好的处理序列的信息,即前面的输入和后面的输入是有关系的。
比如,当我们在理解一句话意思时,孤立的理解这句话的每个词是不够的,我们需要处理这些词连接起来的整个序列;
当我们处理视频的时候,我们也不能只单独的去分析每一帧,而要分析这些帧连接起来的整个序列。
以 np 的一个最简单词性标注任务来说,将 我 吃 苹果 三个单词标注词性为 我/nn 吃/v 苹果/nn。
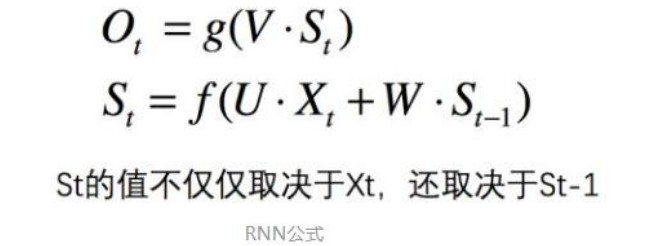

RNN 手写数字识别
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取mnist数据集,one_hot=True将y列编码为维度10分类的0,1编码
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data_bak', one_hot=True)
# 打印输出训练集的形状(55000, 784)
print(mnist.train.images.shape)
# 超参数
lr = 0.001
training_iters = 1000000
batch_size = 128
n_inputs = 28
n_steps = 28
n_hidden_units = 128
n_classes = 10
# 图输入
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, n_inputs])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes])
# 定义权重
weights = {
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_units, n_classes]))
}
biases = {
'out': tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[n_classes, ]))
}
def RNN(X, weights, biases):
# 单元
# forget_bias = 1.0 是初始值
# lstm_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(n_hidden_units, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True)
rnn_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(n_hidden_units)
# lstm cell 分为两部分 (c_state, m_state), RNN会计算每一个cell里面的结果
# _init_state = lstm_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
_init_state = rnn_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
# states里面(c_state, m_state),如果只是一般的RNN的话,就只是m_state
# states是最后一个state,outputs是个list,每一步的output都存在里面
# 有rnn和dynamic_rnn,区别是每批次的维度可以不一样,rnn必须一样
# 28 steps就是我们的time轴,time_major是不是第一个维度,我们的是在维度为2的地方,所有False
# outputs, last_states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(lstm_cell, X, initial_state=_init_state, time_major=False)
outputs, last_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(rnn_cell, X, initial_state=_init_state, time_major=False)
# 如果是True,outputs的维度是[steps, batch_size, depth],反之就是[batch_size, steps, depth]。就是和输入是一样的
# last_state就是整个LSTM输出的最终的状态,包含c和h。c和h的维度都是[batch_size, n_hidden]
# 隐藏层到输入结果
# results = tf.matmul(last_states[1], weights['out']) + biases['out']
results = tf.matmul(last_state, weights['out']) + biases['out']
return results
pred = RNN(x, weights, biases)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=y))
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(cost)
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
step = 0
while step * batch_size < training_iters:
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
batch_xs = batch_xs.reshape([batch_size, n_steps, n_inputs])
test_batch_xs, test_batch_ys = mnist.test.next_batch(batch_size)
test_batch_xs = test_batch_xs.reshape([batch_size, n_steps, n_inputs])
_, = sess.run([train_op], feed_dict={
x: batch_xs,
y: batch_ys
})
if step % 20 == 0:
print("Train set accuracy %s" % sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
x: test_batch_xs,
y: test_batch_ys
}))
step += 1
test_xs, test_ys = mnist.test.next_batch(128)
test_xs = test_xs.reshape([-1, n_steps, n_inputs])
print("Test set accuracy %s" % sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
x: test_xs,
y: test_ys
}))
