Linux文件系统
- 文件名名称严格区分字符大小写;
- 文件可以使用除了
/以外的任意字符; - 文件名长度不能超过255个字符;
- 以
.开头的文件为隐藏文件,除了:-
.:当前目录 -
..:当前目录的上一级目录
-
工作目录: working directory
家目录: home
常用命令:
pwd
- printing working directory(显示工作目录)
cd
change directory(切换目录)
cd [/PATH/TO/SOMEDIR]-
cd或cd ~切换用户的家目录 -
cd ~USERNAME: 切换至指定用户的家目录 -
cd -:在上一次所在目录与当前所在目录来回切换 - 相关的环境变量:
-
PWD当前工作目录,$PWD -
OLDPWD上一次的工作目录,$PLDPWD
-
ls
list,列出指定目录下的内容
-
ls [OPTION]... [FILE]...
-
-a:显示所有文件,包括隐藏文件
-
-A:显示 除了.和..之外的所有文件
-
-l: --long,长格式列表,即现时文件的详细属性信息;
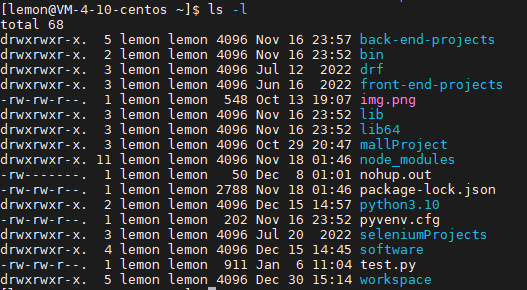
- d: (第一个字段)文件类型,还有-,d,b,c,l,s,p
- -代表是常规文件,
- d代表是文件夹-目录文件,
- -b代表block device块设备文件、支持以block为单位进行随机访问,
- -c代表character device字符设备文件、支持以character为单位进行线性访问)
- major number:主设备号,用标识设备类型,进而确定要加载的驱动程序
- minor number:次设备号,用于标识同一类型中的不同设备
- -l:symbolic link,符号链接文件
- -p:pipe,命名管道
- -s:socket,套接字文件,两个文件进行通信
- rwxrwxr-x.
- 左三位rwx:文件属主的权限;
- 中三位rwx:文件属组的权限;
- 右三位r-x:其他用户(非属主/属组)的权限;
- 末尾如果还有点号
.,说明文件还有隐藏属性 - 4096:数字代表文件的大小,单位是字节
- Nov 16 23:57: 文件最后一次修改的时间
-
-h, --human-readable:对文件大小进行单位换算;换算后的结果可能会是非精确值
-
-d:查看目录自身而非其内部的文件列表
-
-r:reberse逆序显示
-
-R:recursive,递归显示
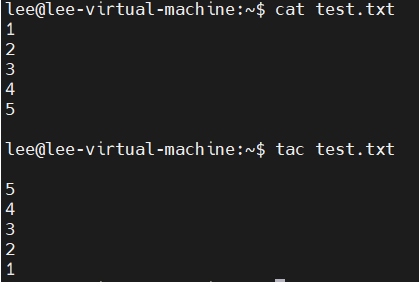
cat
concatenate
- 文件文本查看工具:
- cat /etc/fstab
- cat /stc/passwd
- cat [OPTION]... [FILE]...
- -n: 给显示的文本行编号
- -E: 显示行结束符$
- tac [OPTION]... [FILE]... // 与cat相比,文件内容是逆序的
- -n: 给显示的文本行编号
- -E: 显示行结束符$
-
file
查看文件内容类型
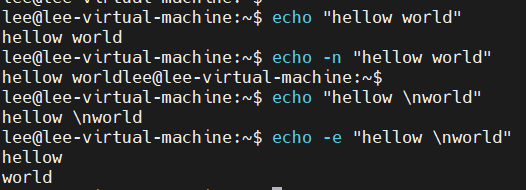
echo
回显
- echo [SHOT-OPTION]... [STRING]...
- STRING可以使用英豪,单引号和双引号均可使用
- 单引号:强引用,变量引用不执行替换
- ~]# ''$SHELL’
- 双引号:弱引用,变量引用会被替换
- ~]# '$SHELL'
- 注意:变量引用的正规符合
${name}
- -n: 不进行换行;
- -e: 让转义符生效
-
关机或重启命令(shutdown)
shuwdown [OPTIONS...][TIME][WALL...]
- OPTIONS:
- -h: halt
- -r:reboot
- -c:cancel
- TIME:
- now
- hh:mm
- +m
- WALL
日期相关命令
Lixun系统启动时从硬件读取日期和时间信息;读取完成以后,就不再于硬件相关联
系统时钟: date
硬件时钟: clock
date
-
显示时间 date [OPTION]... [+FORMAT] 设定日期时间 date [-u|--utc|--universal] [MMDDhhmm[[CC]YY][.ss]] -
ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date 2023年 02月 27日 星期一 22:34:46 CST ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%F 2023-02-27 ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%H 22 ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%c 2023年02月27日 星期一 22时35分08秒 ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%H 22 ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%Y 2023 ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%M 35 ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%m 02 ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%S 44 ubuntu@VM-0-6-ubuntu:~$ date +%s 1677508570
clock, hwclock硬件时钟
- 显示或设定硬件时钟
- -s, --htcosys;以硬件为准,把系统调整为硬件时间相同;
- -w, --systohc;以系统为准,把系统调整为系统时间相同;
cal
日历
cal [[month] year]
which
-
which - shows the full path of (shell) commands
-
which [options] programname [...]
- --skip-alias:忽略别名
[root@rhino014 ~]# which ls alias ls='ls --color=auto' /usr/bin/ls [root@rhino014 ~]# which --skip-alias ls /usr/bin/ls
whereis
whereis - locate the binary, source, and manual page files for a command(能显示二进制文件、源码文件、手册页)
man whereis 查看可选项:
SYNOPSIS
whereis [options] [-BMS directory... -f] name...
OPTIONS
-b Search only for binaries.
-m Search only for manuals.
-s Search only for sources.
-u Only show the command names that have unusual entries. A command is said to be
unusual if it does not have just one entry of each explicitly requested type. Thus
'whereis -m -u *' asks for those files in the current directory which have no docu‐
mentation file, or more than one.
-B list
Limit the places where whereis searches for binaries, by a whitespace-separated list
of directories.
-M list
Limit the places where whereis searches for manuals, by a whitespace-separated list
of directories.
-S list
Limit the places where whereis searches for sources, by a whitespace-separated list
of directories.
-f Terminates the directory list and signals the start of filenames. It must be used
when any of the -B, -M, or -S options is used.
-l Output list of effective lookup paths the whereis is using. When non of -B, -M, or
-S is specified the option will out hard coded paths that the command was able to
find on system.
运用测试:
[root@rhino014 ~]# whereis -b ls # 仅搜索二进制文件路径
ls: /usr/bin/ls
[root@rhino014 ~]# whereis -m ls # 仅搜索使用手册文件路径
ls: /usr/share/man/man1/ls.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1p/ls.1p.gzwho
who - show who is logged on
who [OPTION]...
- -b 系统此次启动的时间
- -r 运行级别
[root@rhino014 ~]# who
root pts/4 2023-03-02 17:49 (192.168.8.5)
root pts/5 2023-03-02 16:35 (192.168.8.5)
You have mail in /var/spool/mail/root
[root@rhino014 ~]# who -b
system boot 2022-10-03 10:30
You have mail in /var/spool/mail/root
[root@rhino014 ~]# who -d
pts/0 2023-03-02 18:24 21113 id=ts/0 term=0 exit=0
pts/1 2023-03-02 18:04 21814 id=ts/1 term=0 exit=0
pts/2 2023-03-02 18:24 26833 id=ts/2 term=0 exit=0
pts/3 2022-10-14 17:11 27715 id=ts/3 term=0 exit=0
pts/6 2022-10-25 16:11 3776 id=ts/6 term=0 exit=0
pts/7 2023-02-20 11:08 30255 id=ts/7 term=0 exit=0
pts/8 2023-02-06 11:59 9349 id=ts/8 term=0 exit=0
pts/9 2022-10-18 17:41 46290 id=ts/9 term=0 exit=0
pts/10 2023-02-06 11:59 15423 id=s/10 term=0 exit=0
pts/11 2022-10-04 12:30 991 id=s/11 term=0 exit=0
pts/12 2023-02-06 09:39 11101 id=s/12 term=0 exit=0
pts/13 2022-10-18 13:23 1726 id=s/13 term=0 exit=0
[root@rhino014 ~]# who -l
[root@rhino014 ~]# who -u
root pts/4 2023-03-02 17:49 . 5156 (192.168.8.5)
root pts/5 2023-03-02 16:35 02:17 43483 (192.168.8.5)
[root@rhino014 ~]# who -r
run-level 5 2022-10-03 10:31w
w - show who is logged on and what they are doing
